Request Information
We're Sorry
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at helpdesk@franklin.edu, 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.

What Is Business Analytics and What Do Analysts Do Exactly?
Data is the fabric of business. Every business decision that’s made is based on “the data” and often the person weaving that fabric is the business analytics professional.
Business analytics involves taking the information culled from collected data points and creating practical, actionable steps a company can take. This can be done through data mining, statistical analysis, data aggregation and other similar tasks.
Business analytics professionals can be found performing these tasks in every industry and across all major business functions including finance, human resources, operations and marketing.
Just like a good business analytics professional, let’s dig deeper into the data to find out what makes this such a compelling career.
The Basics of Business Analytics
Business analytics is the application of data to solve business challenges and help the company make strategic business decisions.
“Business analytics professionals focus on creating solutions and solving existing challenges that are unique to the business,” Jiang Li, Ph.D., chair, M.S. in Business Analytics and lead faculty, M.S. in Data Analytics at Franklin University, says. “They explore data and utilize, manipulate and apply well-established data models based on different business scenarios to make decisions.”
Three Types of Business Analytics
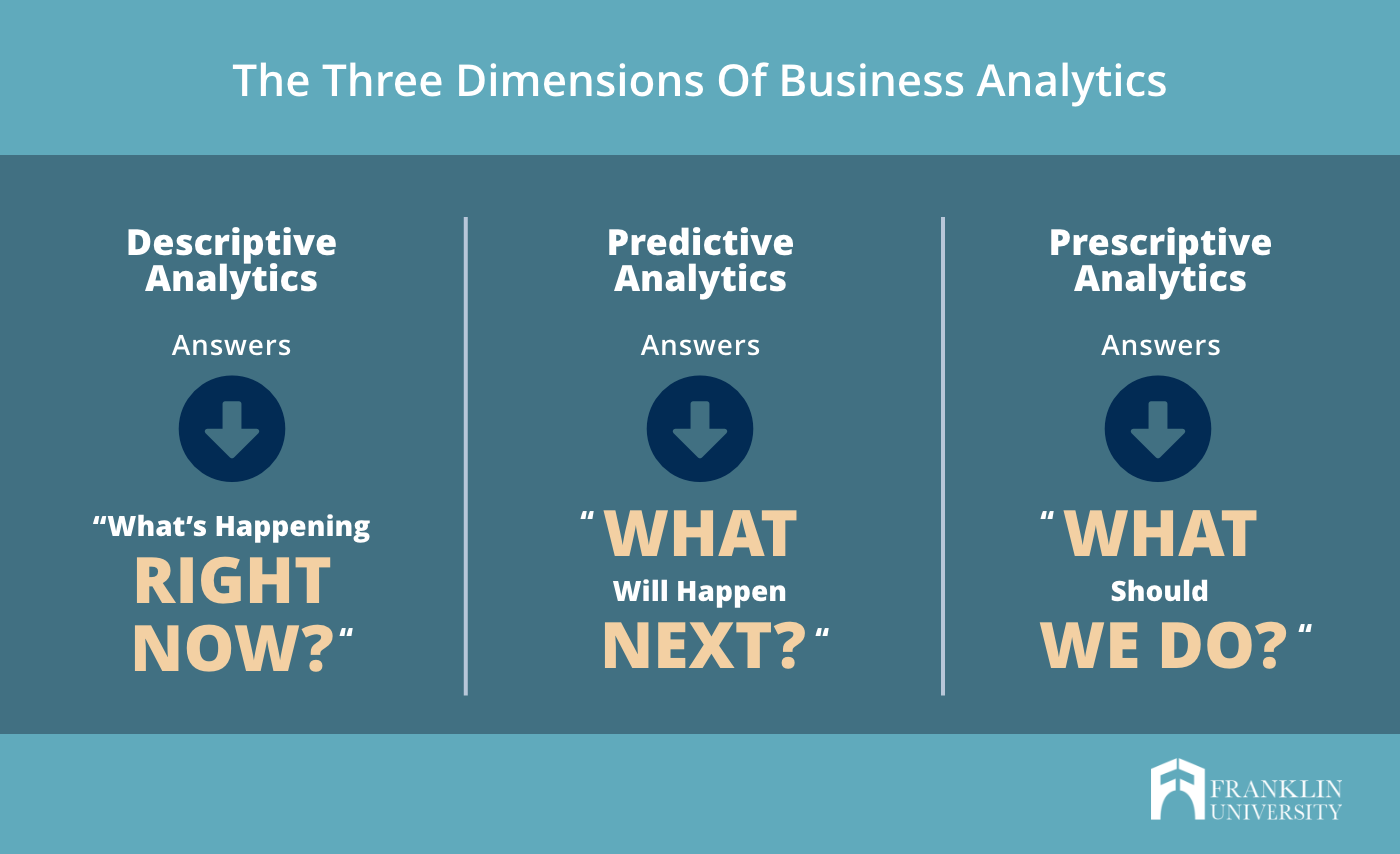
Descriptive Analytics offers a look into past and current trends and patterns. While it’s often used to look at the current state of the business, it can also help provide some historical context for how the company reached its current position.
Predictive Analytics is really the nexus of analytics reporting. The data mining done here isn’t as deep but it is robust as it offers a way to visualize various sub-groups of information as you attempt to look at specific sections of the bigger picture. It’s also used as a baseline for prescriptive analytics reporting.
Prescriptive Analytics combines analytics modeling with probability matrices in an attempt to forecast future trends and market patterns. Because you’ll rely on a wide swath of information, these analytics charts will need to be continually reviewed, and potentially adjusted, as new information is made available.
Get a FREE roadmap that includes insider information to help you maximize the many opportunities in the fast-growing field of Big Data.
Common Questions That Business Analysts Routinely Address
Whether it’s driving operational efficiencies, informing products or services, improving customer experiences, determining pricing or other facets of business that drive competitive advantages—a business analyst is at the heart of change.
Business analysts (BAs) may help organizations answer critical questions like:
- What is preventing us from reaching our objectives?
A business analyst may work with executive and core functional stakeholders in a business to chart strategic objectives. Then, the analyst will sift through company data to determine how likely they are to reach those objectives. - How should we invest to improve the digital experience for our customers?
The business analyst may work with IT leaders and business stakeholders (such as marketing or executives) to define the requirements, scope and investment threshold for new digital products or projects. - What strategies should we use to increase our profit margin?
The business analyst may work with operational leaders, and business performance data to identify the levers that impact profit margin; identifying key strategies and modeling subsequent results to show the impact of change. - Who should we target with our marketing campaigns? What types of people are most likely to be our customers?
BAs may lead quantitative research studies to identify valuable customer segments for the business. - How big is the addressable market for our growth and are we poised to win?
It may be important for a business analyst to be able to identify the size of a market for a business as well as assess the businesses competitive advantage in the market (pricing, positioning, etc.). - Are we utilizing, rewarding and retaining our people effectively?
Collecting and analyzing HR data to make recommendations related to recruitment, retention and legal compliance could be a function performed by a business analytics professional. Using that data can enable the HR team to objectively see the entire hiring process and find areas where it could be strengthened in order to increase employee retention and happiness.
Business analytics professionals usually work with many different business roles, including more technical roles such as an engineer or data scientist and less technical roles such as managers, directors, and team leads. The knowledge that each of those roles holds is critical for business analytics professionals to learn so that they can build an in-depth understanding of the whole business. That knowledge also helps with business problem-solving which highly depends on domain knowledge.
What It Takes To Be A Successful Business Analyst
To accomplish this highly critical and often complex work, business analysts must be able exhibit a core set of skills.Successful business analysts must be able to:
- Understand business requirements and assess processes to understand how data-driven changes can improve efficiency and add value.
- Determine practical implications of data analysis, including what’s technologically feasible and financially reasonable.
- Collect and mine the right types of data to definitively answer specific questions or solve critical problems.
- Use technology to scale or speed up data discovery and insights.
- Deliver defensible data-driven recommendations and reports to executives and stakeholders.
- Organize stakeholders, research and tech teams to understand what’s needed, valued and prioritized when it comes to information.
The Skills Needed To Be A Successful Business Analyst

To be a successful business analytics professional you will need to master several base-level skills including:
- Database languages (SQL, etc.) to retrieve and explore data.
- Programming languages (R, Python) to create and apply computer algorithms.
- Data manipulation (Excel and SAS) is necessary to conduct descriptive and predictive analytics.
- Forecasting, budgeting and financial analysis brings into focus the business financial performance. This information will lead to some of the most consequential decisions a business makes.
- Business management theory in order to identify and analyze areas of the business in order to maximize the success of organizational strategies.
- Data visualization (Tableau & Microsoft Power BI) to elevate the right information to senior leadership.
Being A Data-Driven Storyteller
The “X-Factor Skill” of a successful business analytics professional? Storytelling. If you can’t effectively tell the story of the data, it will be difficult to get any traction on the solutions you propose.
Melissa Schafer agrees. Schafer, the data scientist senior manager at National General Insurance Company, says “You can be the smartest person in the company, build the best models, and be an expert programmer, but if you cannot explain yourself well and facilitate understanding by leadership, then your work product will never be used.”
A Field of Opportunity
Are you ready to make a change?
Business analytics is a diverse career field full of opportunity. You can kick-off your career with the Business Analytics Program at Franklin University. The program provides industry-relevant curriculum with the ability to customize your learning plan through electives that align with your interests.





